The Nigeria Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (NCDC) has attributed the rise in Lassa fever cases to the effects of climate change. The NCDC Director-General, Ifedayo Adetifa, highlighted that changing weather patterns have created conditions favorable for the proliferation of rodents, which are the primary carriers of the Lassa fever virus.
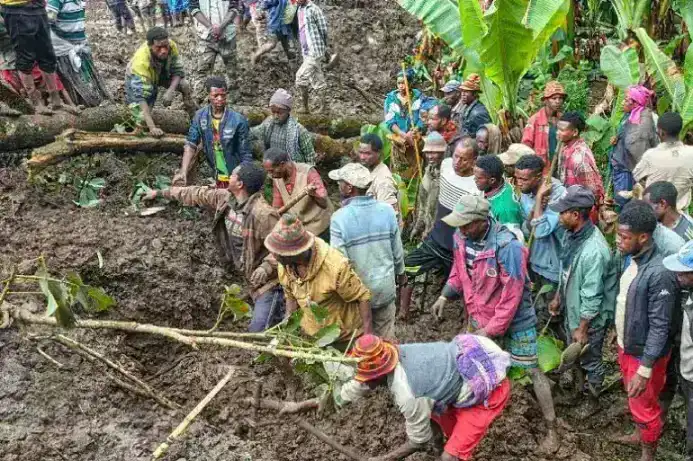
Lassa fever, an acute viral hemorrhagic illness, is endemic in Nigeria, particularly in states like Edo, Ondo, and Ebonyi. According to recent data from the NCDC, the country has recorded over 8,000 suspected cases and more than 1,200 confirmed cases this year alone. The fatality rate remains concerning, with an average of 17%.
Climate change has exacerbated the risk factors for Lassa fever transmission. Increased rainfall and rising temperatures have contributed to rodent population growth and migration into human habitats, intensifying human-rodent contact.
NCDC’s Preparedness and Response
The NCDC is ramping up efforts to address the resurgence of Lassa fever. Key strategies include strengthening surveillance, providing rapid diagnostic testing kits, and enhancing treatment protocols in affected regions. Additionally, the agency is collaborating with international partners to conduct research aimed at understanding the impact of climate change on infectious disease dynamics.
Public health campaigns remain central to the NCDC’s approach, focusing on promoting preventive measures such as proper food storage, maintaining hygienic environments, and minimizing exposure to rodent-infested areas.
Broader Implications for Nigeria
The surge in Lassa fever cases underscores the intersection of climate change and public health challenges. As Nigeria continues to face the impacts of global warming, experts warn of potential increases in other climate-sensitive diseases such as malaria and cholera.
To combat these challenges, stakeholders are calling for a comprehensive approach that integrates climate adaptation strategies into national health policies. The federal government has also been urged to allocate more resources to climate-resilient health systems and research initiatives.
The NCDC has emphasized the importance of community engagement in controlling Lassa fever outbreaks. By adopting preventive measures and promptly reporting suspected cases, communities can play a pivotal role in mitigating the spread of the disease.