Nigeria, Africa’s most populous nation and largest economy, has been grappling with rising inflation, which has surged alarmingly in recent years. The inflation rate has significantly affected various sectors, from agriculture to manufacturing, raising concerns about economic stability and the future of businesses operating in the country.
Inflation Trends
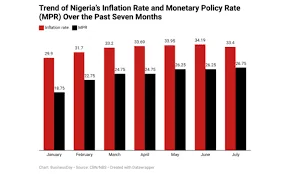
Inflation in Nigeria has been a persistent challenge, with rates soaring to double digits. According to the National Bureau of Statistics, the inflation rate reached a staggering 22.79% in September 2023, driven by rising food prices and supply chain disruptions. This trend is not new; Nigeria has faced inflationary pressures for decades, often exacerbated by external factors like global oil prices and internal issues such as inadequate infrastructure and poor governance.
Effects on Agriculture
The agricultural sector, which employs a significant portion of Nigeria’s workforce, has been particularly hard hit. Rising costs of inputs such as seeds, fertilizers, and pesticides have made it increasingly difficult for farmers to maintain profitability. For instance, the price of fertilizer, a crucial component for boosting crop yields, has skyrocketed, pushing many farmers to reconsider their planting strategies.
As a result, some farmers have resorted to subsistence farming, focusing on producing just enough food for their families rather than cultivating surplus for sale. This shift not only threatens food security in the country but also undermines the agricultural sector’s potential as a driver of economic growth.
Manufacturing Sector Challenges
The manufacturing sector is not exempt from the repercussions of rising inflation. Increased production costs have led to reduced profit margins, forcing manufacturers to make tough decisions about scaling back operations or passing costs onto consumers. Local manufacturers often struggle to compete with cheaper imported goods, which may further impact their market share.
In recent months, several manufacturing companies have reported layoffs and reduced workforce hours, highlighting the fragility of the industry. Companies that once thrived are now at risk of closure due to rising operational costs and an inability to adapt to the volatile economic landscape.
Consumer Behavior Changes
Inflation has also transformed consumer behavior across Nigeria. With disposable income shrinking, many consumers are adjusting their spending habits. There has been a noticeable shift towards budget shopping, with discount stores and markets seeing a surge in patronage. This change presents both challenges and opportunities for retailers.
Retail businesses must adapt to this new consumer landscape, focusing on offering value-oriented products and services. Companies that can efficiently manage their supply chains and keep prices competitive are more likely to survive in this inflationary environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the rising inflation in Nigeria poses significant challenges for businesses across various sectors. From agriculture to manufacturing and retail, the economic climate is forcing companies to rethink their strategies to remain viable. To navigate this uncertain landscape, Nigerian businesses must prioritize adaptive strategies, including cost management, innovation, and improved supply chain efficiency. As inflation continues to shape the economic reality, it is crucial for businesses to remain resilient and proactive in the face of these challenges.